¶ Dihexa (PNB-0408)
¶ At a Glance
Dihexa (N-hexanoic-Tyr-Ile-(6) aminohexanoic amide) is a synthetic oligopeptide designed to repair brain damage and restore memory. Unlike traditional nootropics that transiently boost neurotransmitters, Dihexa is a "structural remodeler"—it mimics Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) to trigger the growth of new connections between neurons (synaptogenesis).
In preclinical models, it was famously cited as being "seven orders of magnitude" (10 million times) more potent than the brain's own growth factor, BDNF, at inducing dendritic spine formation. However, its immense potency comes with a critical caveat: its mechanism involves activating c-Met, a pathway also used by certain cancers to grow and spread.
¶ Safety Status
Dihexa is an unapproved research chemical. While short-term animal studies showed no toxicity, its primary mechanism (c-Met activation) is theoretically linked to oncogenesis. There is no long-term human safety data.
¶ Protocol Card
- Standard Dose: 10–20 mg per day.
- Routes: Oral (capsules) or Transdermal (dissolved in DMSO).
- Timing: Morning or afternoon (non-stimulatory).
Critical Cycling (The Accumulation Risk)
- Half-Life Warning: Dihexa has an extremely long terminal half-life in rodents (~12 days). Daily dosing may lead to significant bioaccumulation.
- Recommended Cycle: Many users pulse dose (e.g., once weekly) or use short cycles (2–4 weeks ON, 4 weeks OFF) to clear the compound.
¶ The Bottom Line
Dihexa is arguably the most potent neurogenic compound available on the grey market. It is capable of profound structural repair in animal models of Alzheimer's. However, the failure of its derivative (Fosgonimeton) in Phase 3 trials and the theoretical cancer risk make it a high-stakes intervention. It is best reserved for severe cognitive deficits rather than casual optimization.
¶ The Benefits (The "Why")
¶ 1. Profound Synaptic Reconstruction
Dihexa's primary claim to fame is its ability to build "hardware" in the brain. Most nootropics (like caffeine or racetams) are like turning up the voltage in a circuit; Dihexa builds new wires.
- Dendritic Arborization: It stimulates the growth of dendritic spines, the tiny protrusions on neurons where synapses form.
- Memory Restoration: In models of neurodegeneration (like scopolamine-induced amnesia), it restored spatial memory to the level of young controls[1][2].
¶ 2. Oral Bioavailability
Unlike many peptides (e.g., Cerebrolysin or Semax) that require injections or nasal sprays, Dihexa was chemically engineered to survive stomach acid and cross the blood-brain barrier when taken orally. This makes it uniquely accessible for a peptide therapeutic.
¶ 3. Non-Stimulatory Focus
Users typically report a "clean" improvement in problem-solving and logical processing without the jitters or crash associated with stimulants. It is often described as providing a background stability to cognition.
¶ Reality Check: Context & Caution
¶ The "Mouse vs. Human" Gap
While the "10 million times more potent than BDNF" figure is technically true for spinogenesis assays in a dish, it does not directly translate to 10 million times more IQ points. The human brain is vastly more complex.
- Clinical Trial Failure: Athira Pharma, the company founded by Dihexa's inventors, developed a modified prodrug called Fosgonimeton (ATH-1017). In September 2024, this drug failed its Phase 2/3 clinical trial (LIFT-AD) for mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease, missing its primary cognitive endpoints[3][4]. This casts significant doubt on whether HGF mimetics can reverse established dementia in humans.
¶ The Cancer Elephant in the Room
The mechanism that makes Dihexa effective (c-Met activation) is the same mechanism that drives the metastasis of many cancers.
- The Risk: c-Met is a proto-oncogene. While Dihexa itself may not cause a new cancer (which usually requires multiple mutations), it could theoretically act as "fertilizer" for existing, undiagnosed micro-tumors, facilitating their spread (metastasis).
- The Defense: The developers argue that transient activation is safe and that safety studies showed no neoplastic induction[5]. However, these studies were short-term. No multi-year carcinogenicity studies exist.
¶ Emotional Blunting ("The Robot Effect")
A distinct side effect reported by biohackers is a reduction in emotional range. Users describe feeling hyper-logical, socially detached, or "autistic-like" during cycles. This may be due to the rapid structural changes in hippocampal or frontal circuits outpacing emotional integration.
¶ Deep Dive: Mechanism & Evidence
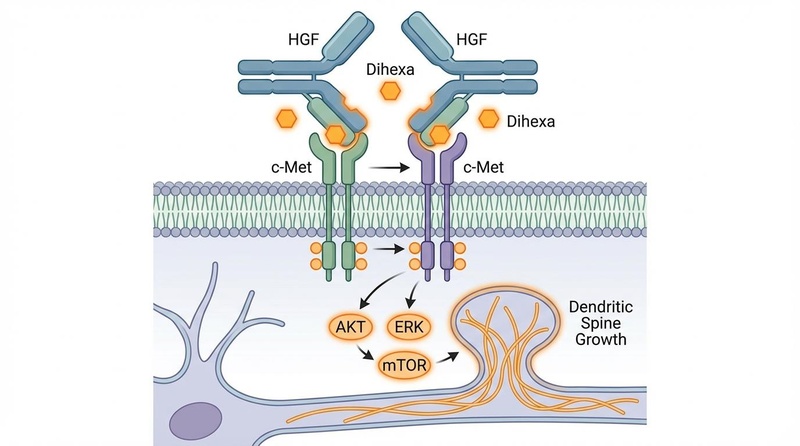
¶ Mechanism of Action: The HGF/c-Met Axis
Dihexa is an Angiotensin IV (AngIV) analog, but it does not work through the classic AT4 receptor system involved in blood pressure. Instead, it functions as a Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) Mimetic.
- Dimerization: HGF is a powerful neurotrophic factor, but it is unstable and difficult to use therapeutically. Dihexa binds to HGF and forces it to form pairs (dimers).
- Receptor Activation: These HGF dimers bind to the c-Met receptor (a tyrosine kinase receptor) on the surface of neurons.
- Signaling Cascade: This activates downstream pathways (PI3K/AKT and ERK/MAPK) that turn on the genes responsible for cell survival and the growth of new synaptic connections[6].
This mechanism is distinct from BDNF mimetics (like 7,8-DHF or Semax), offering a unique pathway for neurorestoration.
¶ Pharmacokinetics: The Accumulation Warning
Dihexa has highly unusual pharmacokinetics for a peptide.
- Metabolic Stability: It is resistant to enzymatic breakdown in the blood (half-life ~5–8 hours).
- Terminal Half-Life: In pharmacokinetic studies on rats, the terminal elimination half-life was found to be approximately 12 days[7].
- Implication: If you take a dose today, half of it may still be in your system nearly two weeks later. Daily dosing can lead to massive accumulation, reaching steady-state levels far higher than intended. This makes the case for pulse dosing (e.g., once a week) scientifically compelling to avoid toxicity.
¶ Comparative Table: Dihexa vs. The Field
| Feature | Dihexa | Semax | Cerebrolysin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Target | c-Met (HGF Mimetic) | Melanocortin / BDNF | Multi-modal (CNTF, GDNF, BDNF) |
| Potency (In Vitro) | Ultra-High (Picomolar) | Moderate | Moderate |
| Route | Oral / Transdermal | Nasal Spray / Sub-Q | IM / IV Injection |
| Half-Life | ~12 Days (Risk of buildup) | Minutes (Acute effects) | Short (Requires daily use) |
| Safety Profile | Caution (Oncogene risk) | High ( decades of use) | High (decades of use) |
| Best For | Severe deficits, structural repair | Focus, mild cognitive support | Stroke, TBI, Dementia |
¶ References
Wright JW, Harding JW. The Brain Hepatocyte Growth Factor/c-Met Receptor System: A New Target for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;45(4):985-1000. ↩︎
McCoy AT, et al. Evaluation of metabolically stabilized angiotensin IV analogs as procognitive/antidementia agents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Jan;344(1):141-54. ↩︎
Athira Pharma. Athira Pharma Announces Topline Results from Phase 2/3 LIFT-AD Clinical Trial of Fosgonimeton for Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease. GlobeNewswire. Sep 03, 2024. ↩︎
NeurologyLive. Synaptic Agent Fosgonimeton Falls Short in Phase 2/3 LIFT-AD Trial for Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer Disease. Sep 04, 2024. ↩︎
Harding JW, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor mimics as therapeutic agents. US Patent 8598118B2. 2013. ↩︎
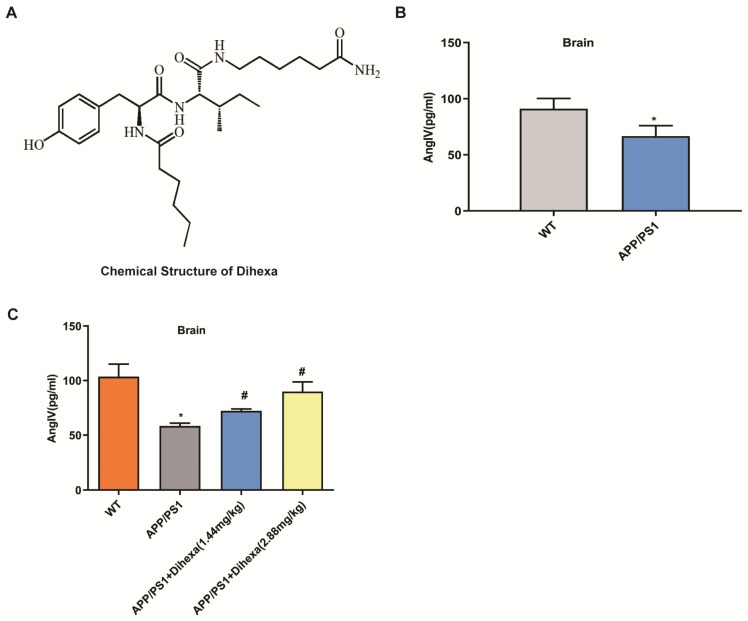
Sun J, et al. AngIV-Analog Dihexa Rescues Cognitive Impairment and Recovers Memory in the APP/PS1 Mouse via the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Brain Sci. 2021 Nov;11(11):1487. ↩︎
Benoist CC, et al. The procognitive and synaptogenic effects of angiotensin IV-derived peptides are dependent on activation of the hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Nov;351(2):390-402. ↩︎