¶ Tesamorelin: Benefits, Dosage, & Side Effects
| Sequence | Hexenoyl-Tyr-Ala-Asp-Ala... (44 AA) |
| Formula | C221H366N72O67S |
| Molar Mass | 5135.9 g/mol |
| Category | GHRH Analog |
| Half-life | 8–30 mins (plasma) |
| Admin | Subcutaneous (SubQ) |
| FDA Status | Approved (Egrifta SV, WR) |
| CAS | 218949-48-5 |
Tesamorelin (Brand names: Egrifta SV, Egrifta WR) is a synthetic analogue of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH). It is the most potent GHRH analogue currently available and the only peptide in its class with FDA approval specifically for reducing excess abdominal visceral adipose tissue (VAT).
Unlike recombinant human growth hormone (hGH), which floods the body with constant levels of hormone, Tesamorelin stimulates the pituitary gland to release GH in a natural pulsatile pattern. This mechanism targets deep abdominal fat while minimizing the side effects—such as insulin resistance and water retention—often associated with direct GH therapy.
¶ At a glance
Aliases
- Brand Names: Egrifta SV, Egrifta WR (F8 formulation)
- Chemical Name: [trans-3-hexenoyl]-hGHRH(1–44)NH2
- Category: Growth Hormone Secretagogue (GHRH Analog)
Key points
- Strongest Benefit: Highly effective at reducing visceral adipose tissue (VAT) by 14–18% over 26 weeks in clinical trials[1][2].
- Secondary Benefit: Significant reduction in liver fat and fibrosis progression in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), with 35% of patients achieving resolution in trials[3].
- Key Limitation: As of 2024/2025, FDA regulations strictly classify it as a "Biological Product," making it ineligible for standard pharmacy compounding and expensive to obtain as a brand-name drug.
- Safety Profile: Generally safer than hGH due to preserved negative feedback loops, though injection site reactions are common and it carries a risk of glucose intolerance.
What people use it for
- Primary Goal: Rapid reduction of stubborn abdominal fat (visceral adiposity).
- Secondary Goals: Improving liver health (NAFLD/NASH), increasing lean muscle mass (mild effect), and optimizing IGF-1 levels for longevity.
- Evidence Quality: High for visceral fat and liver health; Low for cognition (recent 2025 data shows no benefit).
¶ Legal & regulatory status
⚠️ CRITICAL INFORMATION: 2024-2025 UPDATE
¶ Regulatory classification
- FDA Status: Approved. Tesamorelin is FDA-approved under the brand names Egrifta SV (daily) and Egrifta WR (weekly, approved March 2025) for the reduction of excess abdominal fat in HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy.
- Compounding Restrictions: In March 2020 (with strict enforcement solidified by 2024), the FDA reclassified Tesamorelin as a Biological Product because it contains more than 40 amino acids (specifically, 44).
- Impact: Biological products are ineligible for compounding under Section 503A (traditional pharmacy compounding). They do not appear on the "Category 1" bulk substance list.
- Result: Legitimate 503A compounding pharmacies have ceased production of generic Tesamorelin. Access is now primarily limited to the expensive brand-name product or "research chemical" sources.
¶ Sports and competition
- WADA Status: Prohibited. Tesamorelin falls under Category S2 (Peptide Hormones, Growth Factors, Related Substances, and Mimetics) of the World Anti-Doping Agency Prohibited List. It is banned at all times (in and out of competition).
¶ What is Tesamorelin?
Tesamorelin is a synthetic 44-amino acid peptide sequence of human Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH) with a generic trans-3-hexenoic acid group added to the N-terminus.
- Structure: The N-terminal modification (hexenoyl moiety) acts as a "shield," protecting the peptide from degradation by the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4).
- Result: This significantly extends its stability and potency compared to native GHRH (which has a half-life of only minutes).
- Mechanism: It binds to GHRH receptors on pituitary somatotrophs, triggering the synthesis and release of endogenous growth hormone in a pulsatile manner.
¶ What are Tesamorelin's main benefits?
¶ 1. Visceral Fat Reduction (High Evidence)
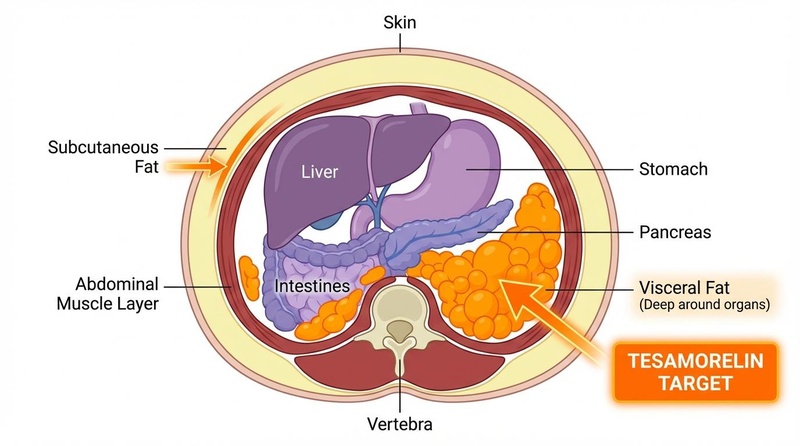
The primary FDA-approved indication for Tesamorelin is the reduction of visceral adipose tissue (VAT)—the deep, metabolically active fat surrounding organs that is linked to cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
- Magnitude: Clinical trials demonstrated a 14–18% reduction in VAT over 26 weeks compared to placebo[1:1][2:1]. Some data indicates a mean reduction of ~35 cm².
- Durability: Fat loss is maintained as long as therapy continues, but VAT tends to return to baseline levels within weeks to months after cessation.
¶ 2. Liver Health & NAFLD (High Evidence)
Tesamorelin has shown potent effects on liver health, making it a leading candidate for treating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH).
- Findings: A landmark randomized trial published in The Lancet HIV (2019) found that Tesamorelin significantly reduced hepatic fat fraction (liver fat) and prevented the progression of liver fibrosis[3:1].
- Resolution: Remarkably, 35% of Tesamorelin-treated subjects achieved NAFLD resolution (liver fat <5%) versus only 4% in the placebo group.
- Mechanism: The reduction in visceral fat decreases the flux of free fatty acids to the liver, while increased GH/IGF-1 directly supports hepatocyte health and oxidative phosphorylation.
¶ 3. Cognition (Low Evidence / Disproven)
Historically, GHRH analogs were hypothesized to improve cognition via increased IGF-1, which promotes neurogenesis.
- Previous Data: A 2012 study in healthy older adults using GHRH showed improvements in executive function and verbal memory[4].
- Recent Findings (2025): A definitive Phase 2 trial by Ellis, Grinspoon et al. (2025) in adults with HIV and abdominal obesity found that while Tesamorelin reduced waist circumference, cognitive benefits did not significantly differ from the control group[5]. This suggests that for established cognitive impairment, Tesamorelin is likely not an effective standalone intervention.
¶ Evidence summary table (human outcomes)
| Outcome / Goal | Effect | Consistency | Evidence Quality | Trials | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visceral Fat (VAT) | High | High | >4 RCTs | FDA-approved indication. 14–18% reduction typically observed. | |
| Liver Fat (NAFLD) | High | High | 2 RCTs | 35% resolution rate vs 4% placebo; prevents fibrosis. | |
| Triglycerides | Moderate | Moderate | Multiple | ~0.6 mmol/L reduction; linked to fat loss magnitude. | |
| Muscle Mass | Moderate | Moderate | 3 RCTs | Increases lean body mass and muscle density; less anabolic than hGH. | |
| Cognition | High | Low | 2 RCTs | Recent 2025 trial showed no significant benefit over placebo. | |
| HbA1c / Glucose | High | High | Multiple | HR 3.3 for diabetes onset; causes mild insulin resistance. |
¶ How does Tesamorelin work?
¶ Pulsatile vs. Continuous GH Elevation
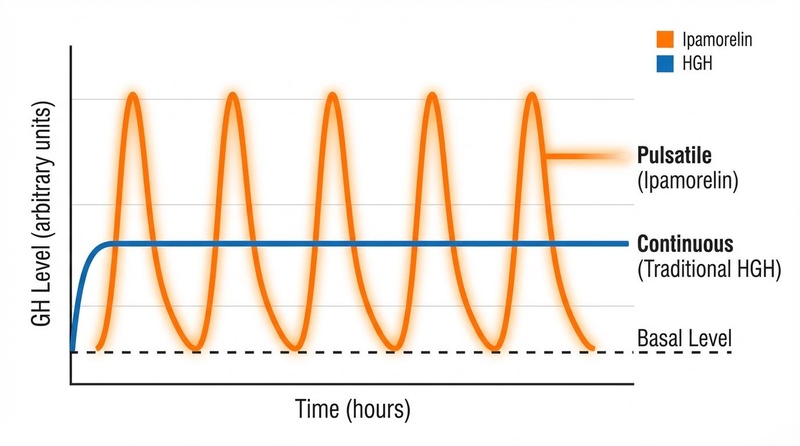
The critical distinction between Tesamorelin and recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) lies in the pattern of hormone exposure:
- Recombinant hGH (Exogenous): Provides a steady, non-physiological elevation of GH levels. This continuous exposure can downregulate receptors and cause side effects like fluid retention (edema), insulin resistance, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Tesamorelin (Endogenous Stimulation): Binds to GHRH receptors on pituitary somatotrophs, triggering them to synthesize and release GH. Crucially, this release remains subject to the body's natural negative feedback loops (via somatostatin).
¶ Pharmacokinetics
- Bioavailability: <4% (SubQ). Despite low bioavailability, the high potency allows the standard dose to be effective.
- Half-life: Elimination half-life is short (~8–12 minutes in healthy subjects, ~26–38 minutes in HIV patients). However, the downstream effect on IGF-1 levels is sustained over 24 hours.
- Metabolism: Degraded by proteolytic enzymes; no specific cytochrome P450 interactions.
¶ Effects on different systems
¶ Metabolic Health
Tesamorelin profoundly impacts metabolic parameters. Beyond VAT reduction, it improves the overall lipid profile, typically lowering triglycerides and total cholesterol. However, it acts as a "double-edged sword" for glucose metabolism; while it reduces insulin-resistant visceral fat, the GH surge itself induces a temporary state of insulin resistance, necessitating monitoring of HbA1c.
¶ Musculoskeletal System
While not as potent as hGH for raw hypertrophy, Tesamorelin increases lean body mass and muscle density (radiographic attenuation). Studies show specific increases in the cross-sectional area of the psoas and rectus abdominis muscles. It is often favored by athletes looking for "dry" gains without the water retention associated with hGH.
¶ Cardiovascular Health
The reduction in visceral fat and liver fat is theoretically cardioprotective. Some studies have shown a reduction in Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (cIMT), a marker of atherosclerosis, though the FDA label notes that long-term cardiovascular safety has not been definitively established.
¶ Administration, reconstitution, and storage
¶ Routes of administration
- Standard: Subcutaneous (SubQ) injection into the abdominal fat.
- Site Rotation: Essential to prevent lipohypertrophy (lumps) or injection site reactions. Rotate sites daily.
¶ Reconstitution
Tesamorelin is supplied as a lyophilized powder.
- Egrifta SV: 2 mg vial. Reconstitute with 1.1 mL (providing ~2 mg/mL). Daily use.
- Egrifta WR: 11.6 mg vial (New 2025). Reconstitute for weekly use.
- Generic/Research: Typically 2 mg or 5 mg vials.
- Technique: Inject bacteriostatic water slowly against the vial wall. Do not shake. Swirl gently until dissolved.
Example reconstitution (Standard 2mg vial):
| Vial Strength | Diluent Added | Final Concentration | Dosage Volume (1mg) | Dosage Volume (2mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | 1 mL | 2 mg/mL | 0.5 mL (50 units) | 1.0 mL (100 units) |
| 2 mg | 2 mL | 1 mg/mL | 1.0 mL (100 units) | 2.0 mL (200 units) |
| 5 mg | 2 mL | 2.5 mg/mL | 0.4 mL (40 units) | 0.8 mL (80 units) |
¶ Storage
- Powder: Store refrigerated (2–8°C). Protect from light.
- Reconstituted:
- Generic/SV: Use immediately or store refrigerated for max 24 hours.
- Egrifta WR: Formulated for multi-dose stability (up to 7 days refrigerated).
¶ Dosage and protocols
¶ FDA Standard Protocol (Egrifta)
- Dose: 2 mg (2,000 mcg) once daily.
- Timing: Subcutaneous injection, ideally in the morning.
- Duration: Clinical benefits in visceral fat are typically seen after 12–26 weeks.
¶ "Anti-Aging" / Body Composition Protocol (Off-Label)
- Dose: 1 mg to 2 mg daily.
- Timing: Often administered before bed to mimic and amplify the body's natural nocturnal GH pulse.
- Cycling: Common protocols involve 5 days on / 2 days off to prevent pituitary desensitization, although clinical trials used continuous daily dosing for 6+ months without efficacy loss.
- Stacking: Frequently paired with Ipamorelin (100–300 mcg).
- Rationale: Ipamorelin inhibits somatostatin (the "brake" on GH), while Tesamorelin hits the accelerator. This theoretically creates a larger GH pulse than either alone.
¶ Safety and side effects
Tesamorelin is generally well-tolerated but carries specific risks monitored by the FDA.
¶ Common Side Effects (>5%)
- Injection Site Reactions: Redness, itching, pain, or nodules (occurring in ~20-50% of patients).
- Arthralgia/Myalgia: Joint or muscle stiffness, usually mild.
- Immunogenicity: Anti-drug antibodies (ADA) develop in approximately 50% of patients. While usually not neutralizing (efficacy remains), they can increase the risk of hypersensitivity reactions.
¶ Metabolic & Glucose Concerns
- Diabetes Risk: The Hazard Ratio for developing type 2 diabetes is 3.3 compared to placebo.
- Mechanism: GH counteracts insulin. Patients may see increased fasting glucose and HbA1c levels.
- Contraindications: Active malignancy (cancer), hypopituitarism, pregnancy (Category X), and known hypersensitivity.
¶ IGF-1 and Cancer
Tesamorelin significantly elevates IGF-1 (often >3 SD above baseline). Because IGF-1 promotes cell growth, there is a theoretical risk of stimulating tumor growth. It is strictly contraindicated in patients with active cancer.
¶ Drug and supplement interactions
- Glucocorticoids: May blunt the GH-releasing effect of Tesamorelin.
- Simvastatin: When co-administered, simvastatin levels may decrease slightly, but usually not requiring dose adjustment.
- Insulin/Hypoglycemics: Tesamorelin may decrease insulin sensitivity, requiring dose adjustments for diabetic patients.
¶ Cost considerations
- Brand Name (Egrifta SV/WR): Extremely expensive, typically $3,000 – $6,000 per month. Insurance coverage is strict (HIV lipodystrophy only).
- Compounded: Since the 2020/2024 biological classification, legitimate compounded Tesamorelin is virtually non-existent in the US.
- Research Chemicals: Grey-market vials range from $40–$80 per 2mg. Risks include lack of sterility, under-dosing, and impurities (e.g., TFA salt content).
¶ Practical FAQ
- How long does it take to see results?
Visceral fat reduction is a slow process. While IGF-1 levels rise within days, significant changes in abdominal fat typically require 12 to 26 weeks of consistent daily use. - Does fat return after stopping?
Yes. Clinical trials showed that visceral fat stores gradually returned to baseline levels after discontinuing treatment. Maintenance protocols or lifestyle changes are necessary to sustain results. - Can I take it if I don't have HIV?
This is "off-label" use. While the mechanism works in healthy adults, the safety data (especially regarding diabetes risk) is drawn primarily from HIV populations. - Is it better than Ipamorelin or CJC-1295?
Tesamorelin is the most potent GHRH analog for fat loss. CJC-1295 is longer-acting but creates a "bleed" of GH rather than a sharp pulse unless combined with Ipamorelin. Tesamorelin's pulsatile nature is superior for lipolysis.
¶ References
Falutz J, et al. (2010). Long-term safety and effects of tesamorelin, a growth hormone-releasing factor analogue, in HIV patients with abdominal fat accumulation. AIDS. PubMed ↩︎ ↩︎
Spooner LM, et al. (2012). Tesamorelin: a growth hormone-releasing factor analogue for the treatment of HIV-associated lipodystrophy. Ann Pharmacother. PubMed ↩︎ ↩︎
Stanley TL, et al. (2019). Effects of tesamorelin on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in HIV: a randomised, double-blind, multicentre trial. Lancet HIV. PubMed ↩︎ ↩︎
Baker LD, et al. (2012). Growth hormone-releasing hormone improves cognitive function in healthy older adults. Arch Neurol. PubMed ↩︎
Ellis RJ, et al. (2025). Effects of Tesamorelin on Neurocognitive Impairment in Abdominally Obese Persons with HIV. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. PubMed ↩︎
Makimura H, et al. (2013). The effects of tesamorelin on body composition and metabolic outcomes in HIV-infected patients. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. PMC ↩︎
Ferdinandi ES, et al. (2007). Preclinical pharmacology and safety of tesamorelin. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. PubMed ↩︎