¶ Cerluten: The Epigenetic Brain Restorer
Source: Bovine Cerebral Cortex (Peptide Complex A-5)
Primary Mechanism: Epigenetic Regulation (Gene Switching)
Standard Dosage: 1–2 capsules (10–20mg) daily
Key Benefit: Long-term neurorestoration and cognitive maintenance
¶ At a Glance
What is it?
Cerluten is a natural peptide complex (designated "A-5") extracted from the cerebral cortex of young calves. It belongs to the "Cytomax" class of Khavinson peptides, which are tissue-specific bioregulators developed in Russia to normalize metabolic processes and protein synthesis in the brain. Unlike synthetic nootropics that force neuronal firing, Cerluten acts as a "gene switch" to restore the structural integrity and function of neurons.
Will it help me?
Cerluten is primarily used for neurorestoration and maintenance. It is best suited for individuals dealing with age-related cognitive decline, recovering from CNS trauma (stroke, TBI), or seeking to preserve "brain reserve" during periods of high stress. It is not a stimulant and does not provide an immediate "buzz."
¶ ⚠️ Safety Status: Generally Safe
Safe: Extensive clinical use in Russia over 30 years with no reported toxic side effects.
Caution: No specific safety data for pregnancy or breastfeeding. Avoid use.
Note: As a bovine extract, it is not vegan.
¶ Protocol Card: The "Khavinson" Cycle
- Format:
- Capsules: 10mg active complex (Standard).
- Lingual: Sublingual drops (Faster absorption).
- Dosage: 1–2 capsules (10–20mg) per day.
- Timing: Take 15–20 minutes before a meal (breakfast or lunch).
- Duration: A standard course is 10–20 days.
- Cycling: Repeat the course every 3–6 months.
- Stacking:
Bottom Line: Cerluten is a "slow" medicine. It works by rebuilding the brain's capacity to heal itself at the genetic level. Think of it as fertilizer for your neurons rather than caffeine for your synapses.
¶ The Contextual Narrative
¶ The "Why": Restoration over Stimulation
Most Western brain supplements (nootropics) focus on increasing neurotransmitters like dopamine or acetylcholine. While effective for short-term focus, they can lead to depletion or tolerance.
Cerluten takes a fundamentally different approach. Based on the "Peptide Regulation of Aging" theory by Professor Vladimir Khavinson, it posits that aging and disease are caused by the silencing of specific genes. Cerluten contains the specific signal peptides that the brain loses with age. By re-introducing these peptides, Cerluten:
- Reactivates specific genes in neurons.
- Restores protein synthesis to youthful levels.
- Normalizes bioelectrical activity in the brain.
This makes it a foundational intervention for longevity rather than just a performance booster.
¶ Reality Check: Managing Expectations
- The "Feel": You likely will not feel Cerluten working in the first few days. There is no jitteriness, no euphoria, and no crash. Users often report a subtle stabilization of mood, "clearer" thinking, and reduced brain fog after the 10-day course is complete.
- The Timeline: Benefits are cumulative. The "after-effect" of a single course can last for 3–6 months as the upregulated gene expression persists.
- The Source: Because it is a natural extraction from animal tissue, there is biological variance. While the "A-5" complex is standardized, it is a soup of many peptides, not a single molecule.
¶ Commercial Context
Cerluten is widely available as a dietary supplement, primarily from vendors specializing in Russian bioregulators.
- Regulatory Status: In Russia, it is approved as a "Parapharmaceutical" (food supplement). In the US and EU, it is unregulated and sold as a supplement or research compound.
- Forms:
- Cerluten (Capsules): The standard "Cytomax" form. Slower acting, longer lasting.
- Cerluten Lingual: Sublingual drops for those who cannot swallow capsules or want faster absorption.
¶ The Evidence Room
¶ Mechanism of Action: Epigenetic Switching
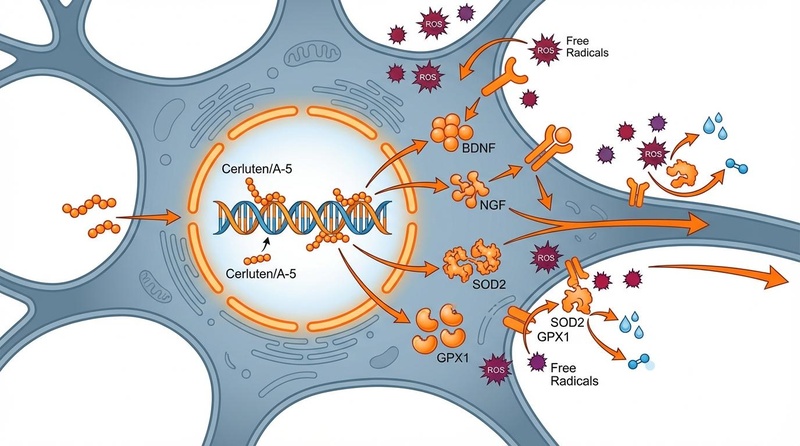
Cerluten functions through a process known as peptidergic regulation of gene expression.
- Nuclear Translocation: Short peptides (2–4 amino acids) within the Cerluten complex penetrate the cell membrane and enter the neuronal nucleus.
- Chromatin Unfolding: These peptides bind to specific binding sites on the DNA promoter regions (specifically in heterochromatin). This interaction causes the unfolding of chromatin (disjoining of the double helix), making the DNA accessible.
- Transcription Initiation: RNA polymerase binds to the exposed DNA, initiating the transcription of mRNA.
- Protein Synthesis: This leads to the synthesis of tissue-specific proteins necessary for neuronal repair and function [1][2].
Specific to the CNS, Cerluten acts as a "neural antioxidant" and structural promoter. Research indicates it upregulates the expression of:
- Antioxidant Enzymes: Superoxide Dismutase (SOD2) and Glutathione Peroxidase (GPX1), which protect neurons from oxidative damage.
- Structural Markers: Nestin (neural stem cells), GAP43 (axonal growth), and β-tubulin III (neuronal cytoskeleton) [1:1][3].
¶ Clinical Research Findings

Note: Most clinical data originates from Russian institutes and manufacturer-sponsored trials. High-quality Western Phase III trials are currently lacking.
¶ 1. CNS Dysfunction and TBI (The 48-Patient Study)
A key study conducted at the St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology evaluated 48 patients with various CNS conditions, including post-stroke states, Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI), and vascular encephalopathy [4][3:1].
- Method: Patients received Cerluten (1–2 capsules, 2–3x daily) for 10–20 days + standard therapy. Control group received only standard therapy.
- Outcomes:
- Good Improvement: 64.6% of Cerluten patients (vs. 27.0% in controls).
- Satisfactory Improvement: 22.9% of Cerluten patients.
- No Effect: 12.5% of Cerluten patients.
- Subjective complaints of memory loss and absent-mindedness dropped from 48.7% to 14.6%.
- Objective EEG readings showed normalization of alpha-rhythm patterns in the cortex.
¶ 2. Cognitive Decline and Aging
In elderly patients and those with cerebral atherosclerosis, Cerluten courses have been associated with improved concentration, emotional stability, and "brain reserve"—the ability of the CNS to withstand stress without decompensation. Studies suggest it can increase "active longevity" by maintaining the functional activity of the brain during aging [5][6].
¶ Comparisons: Cerluten vs. Other Brain Peptides
| Feature | Cerluten | Pinealon | Cortexin | Cerebrolysin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Natural Complex (Cytomax) | Synthetic Tripeptide (Cytogen) | Natural Complex | Natural Complex + Amino Acids |
| Active Sequence | Complex A-5 | Glu-Asp-Arg | Complex | Complex |
| Route | Oral / Sublingual | Oral / Sublingual / Injection | Injection Only (IM) | Injection Only (IV/IM) |
| Best For | Maintenance, Anti-Aging, Prevention | Acute Focus, Circadian Rhythm, TBI | Acute Stroke, Severe TBI | Dementia, Stroke, Recovery |
| Speed | Slow (Cumulative) | Fast (Hours/Days) | Fast | Fast |
| Evidence | Tier 3 (Russian Trials) | Tier 3 (Russian Trials) | Tier 2 (Regional Guidelines) | Tier 1 (Meta-Analyses) |
- Vs. Pinealon: Pinealon is the synthetic version of the active center found in Cerluten. Pinealon acts faster and is better for "crunch time" focus. Cerluten is broader and better for long-term rebuilding.
- Vs. Cortexin: Cortexin is essentially the injectable medical drug version of Cerluten. If you have a severe acute condition (like a recent concussion), Cortexin is the medical standard. Cerluten is the oral alternative for recovery and maintenance.
¶ Safety and Toxicology
- Toxicity: Acute toxicity studies show that even at doses exceeding the therapeutic dose by 1000x, no toxic effects were observed [4:1].
- Side Effects: Extremely rare. Potential for mild allergic reaction to capsule components.
- Contraindications: Pregnancy and lactation (due to lack of data).
¶ References
Khavinson, V. K. (2002). Peptides and Ageing. Neuroendocrinology Letters, 23(Suppl 3), 11-144. Link ↩︎ ↩︎
Khavinson, V. K., et al. (2021). Peptide Regulation of Gene Expression: A Systematic Review. Molecules, 26(22), 7053. Link ↩︎
Khavinson, V. K., & Malinin, V. V. (2005). Gerontological aspects of genome peptide regulation. Karger Publishers. Link ↩︎ ↩︎
St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology. (2006). Clinical Study Report: Efficacy of Cerluten in Patients with CNS Pathology. Medical Center of the Institute. Link ↩︎ ↩︎
Korkushko, O. V., et al. (2011). Geroprotective effect of peptide preparations of the pineal gland and brain in elderly people with accelerated aging. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 151(3), 343-347. Link ↩︎
Khavinson Peptides. (n.d.). Cerluten: Clinical Studies and Application. BioLongevity Labs. Link ↩︎